What is marketing psychology?
Marketers and psychologists have one major thing in common: they both analyze the human mind. When we buy, we play mind games. For this reason, the most popular and most effective ads often blow one’s mind, sometimes literally.
We can only guess what psychological experiments businesses carry out in their laboratories, away from prying eyes, in order to create more advanced mind games and help marketers stay on top.
But marketers and advertisers of all generations have always been eager to find out why people buy what they buy. Let’s analyze well-known marketing psychology techniques in this guide.
7 Most Common Marketing Psychology Practices
Marketing psychology is a science that researches consumer behavior and buying decisions. Over the years, psychology and marketing professionals have worked out numerous revolutionary ideas that have been translated into major methods to influence consumers' decisions.
Reciprocity
Reciprocity is a norm used in different fields of social, psychological, and scientific studies. Austrian economists Ernst Fehr and Simon Gächter, in a paper for the Journal of Economic Perspectives, write:
Reciprocity means that in response to friendly actions, people are frequently much nicer and much more cooperative than predicted by the self-interest model; conversely, in response to hostile actions they are frequently much more nasty and even brutal.
Reciprocity in marketing means giving something to potential and current customers without forcing them to purchase products or services or take part in promoted activities.
Decoy Effect (Asymmetric Dominance Effect)
In an abstract titled Adding Asymmetrically Dominated Alternatives: Violations of Regularity and the Similarity Hypothesis, John Huber, John W. Payne, and Christopher Puto write:
An asymmetrically dominated alternative is one that is dominated by one item in the set but not by another. It is shown that the addition to a choice set of such an alternative can increase the probability of choosing the item that dominates it.
In other words, the decoy effect explains a consumer's decision-making process when an asymmetrical product alternative (that differs from other products in price, features, and other characteristics) is introduced to a set.
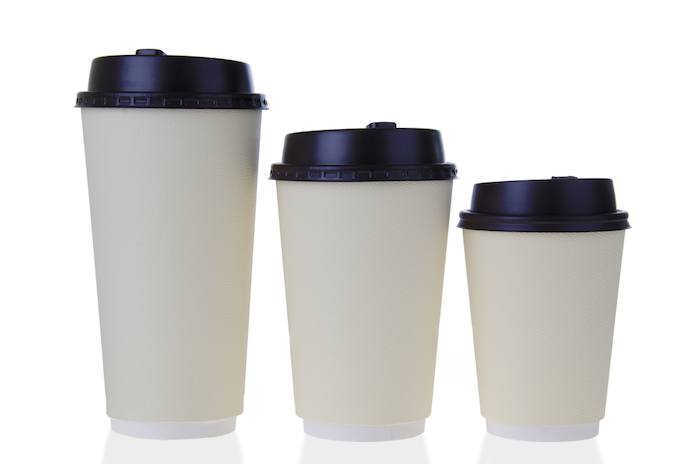

A decoy can be set in different ways. Usually, this trick is used with a set of three products.
Color Psychology
People love colors. At least once, someone asked you about your favorite color. Color is a wonderful instrument for influencing people and creating associations in their minds.
Over the years, scientists have figured out that people have different associations with different colors.
For example, psychology marketing research published in Chemosensory Perception shows how colors make people change their perceptions and preferences about food and beverages.

If you take a look at the infographic created by The Logo Company, you’ll see that brands choose their colors for particular reasons. Unconsciously, people take something they need from brands, and colors play an important role.
Loss Aversion
According to this concept developed by Daniel Kahneman and Amos Tversky, people think that it’s better not to lose anything than to gain something. In other words, we tend to avoid risk and avert loss to save what we’ve already acquired.
The best example of loss aversion in digital marketing psychology is a free trial period. When someone subscribes to a service, they may want to acquire a paid subscription in order not to lose exclusive features.
Social Proof
The term social proof was coined by Robert Cialdini in his book Influence. Social proof demonstrates that people who are uncertain in their behavior tend to copy the behavior of people they like or trust. The best examples of using psychology in marketing in the form of social proof are likes, shares, impressions, followers, views, and comments.
Scarcity
Scarcity is one of the traditional psychological marketing tricks that’s very popular during special sales. To lure customers’ attention and awaken interest, businesses use countdowns, limited edition products or services, demand stickers, and many other effective methods.
Anchoring
In 1974, Kahneman and Tversky (who came up with the loss aversion concept) first theorized the anchoring effect in their paper called Judgment under Uncertainty: Heuristics and Biases.
Anchoring is one of the most popular psychological factors in marketing that influences profits of big companies and small businesses all around the world. Once a product or service is established as being within a certain set, an anchor serves as a cognitive bias that makes consumers consider it based on comparative values rather than intrinsic.
Practice Psychology in Your Marketing with Artificial Intelligence
The importance of psychology to marketing specialists is enormous. Nowadays, advertisers and marketers use lots of psychological tricks to persuade their customers to buy and order products and services.
Want to take advantage of one of the psychology methods we’ve mentioned in practice?
Do it by creating video ads with the Softcube artificial intelligence platform. Softcube will help you edit your footage fast and skilfully with minimum human interaction, allowing you to create high-quality video ads for any purpose and for an image-sized budget.